Anatomy
C5, 6 from Upper trunk
Posterior triangle
- arises upper trunk and passes backward through posterior triangle
- under belly of omohyoid
- deep to trapezius to the suprascapular notch
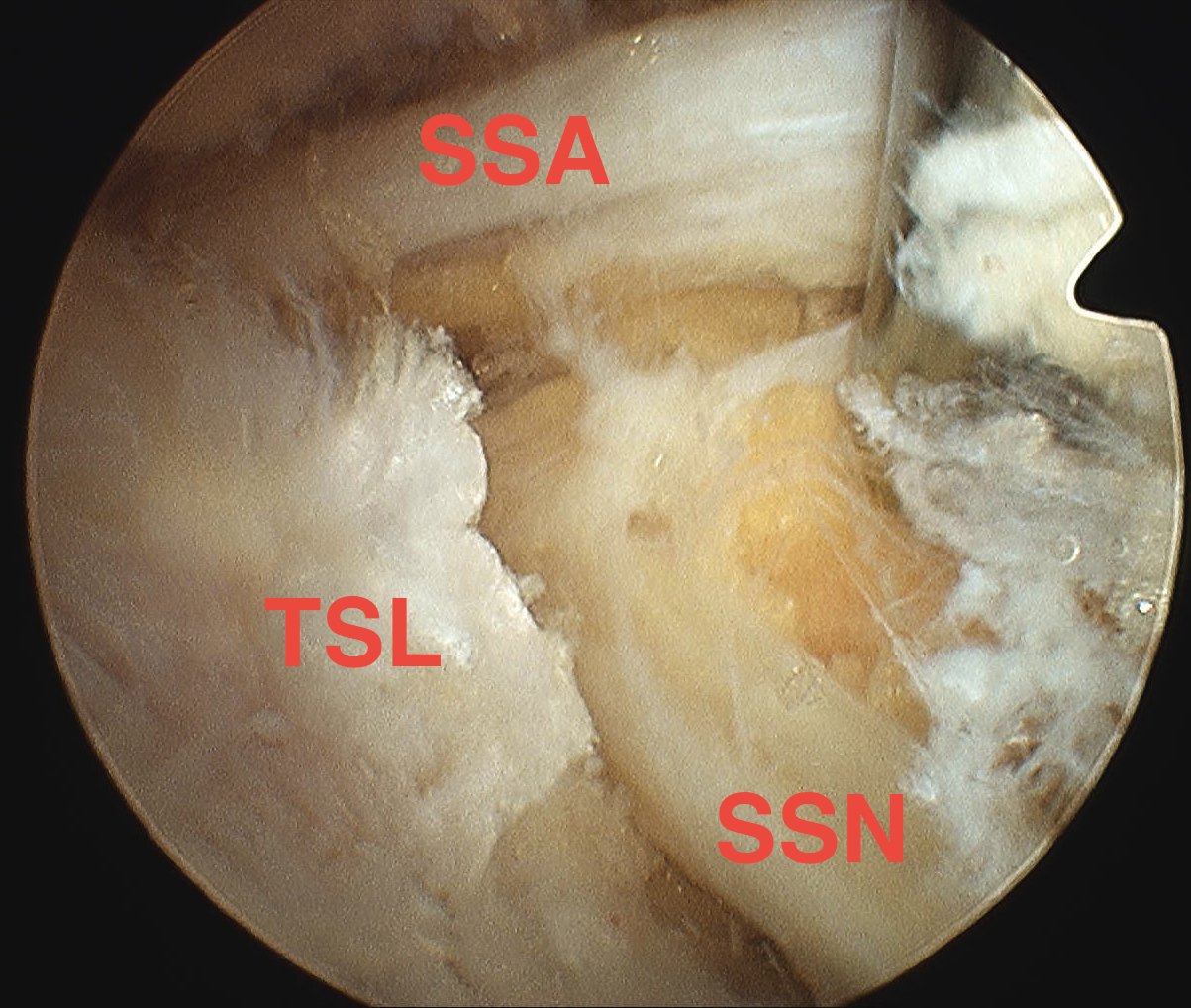
Runs through suprascapular notch
- under superior transverse scapular ligament
- suprascapular artery and vein run over this ligament
- supplies SS 1 cm after passing under ligament
- give articular branch to the shoulder
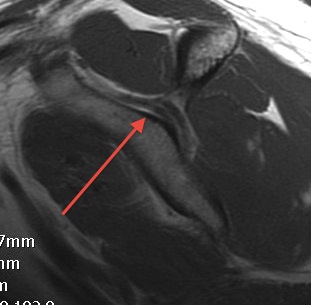
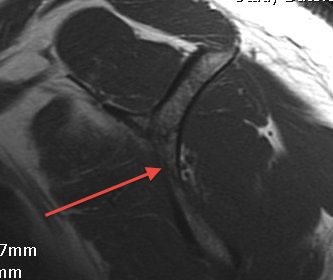
Passes around lateral border spinous process / Spinoglenoid notch
- under spinoglenoid ligament
- inferior transverse scapular ligament
- supplies IS
Motor
- supplies supraspinatus & infraspinatus
Sensory
- ACJ, GHJ
- CA and CH ligaments
Sites of Compression / Injury
Suprascapular notch
- weakness wasting SS & IS
Causes
- trauma most common / driect blow / clavicle or scapula fracture
- iatrogenic / excessive rotator cuff release
- athletes / repetitive overhead motion
Spinoglenoid notch
- weakness wasting IS
Causes
- spinoglenoid cyst associated with superior labral tear / horizontal cleavage / acts as one way valve
- posterior approach to shoulder - > 1 cm medial to glenoid neck
- posterior shoulder OA causing a cyst
History
Pain at back of shoulder
Weakness
Examination
Weakness
Atrophy SS/IS
Atrophy of IS alone
DDx
Rotator Cuff tear
MRI
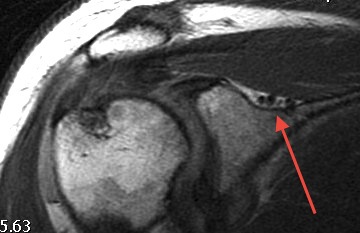
1. Spinoglenoid cyst / labral tear
- may be better seen with MRA
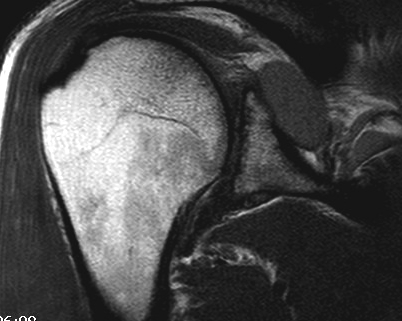
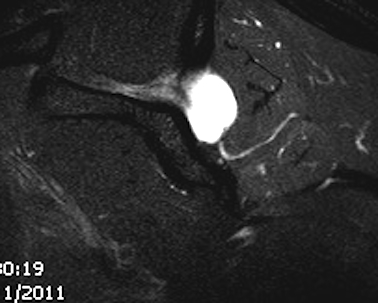
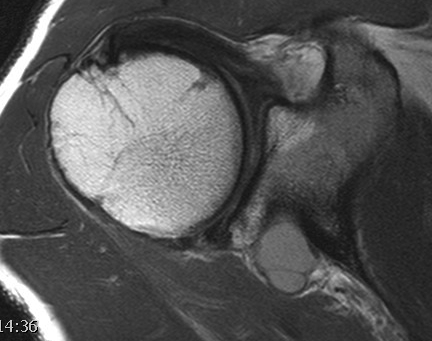
2. Atrophy of SS / IS
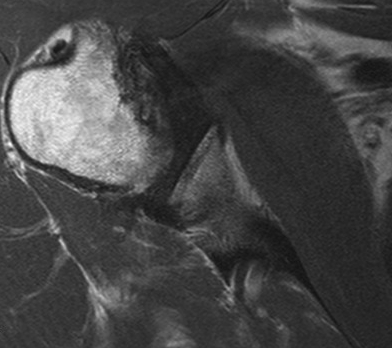
3. Exclude cuff tear
EMG
Demonstrate denervation SS/IS or IS alone
HCLA
Inject SS nerve at suprascapular notch
Management
Non Operative
Reasonable if no ganglion cyst
- a neuropraxia which usually resolves
- avoid overhead activities if possible
- 6 - 9 months
Operative
Spinoglenoid Cyst
1. Secondary to superior labral tear
Majority of cases
A. Cyst Decompression + Arthroscopic labral repair
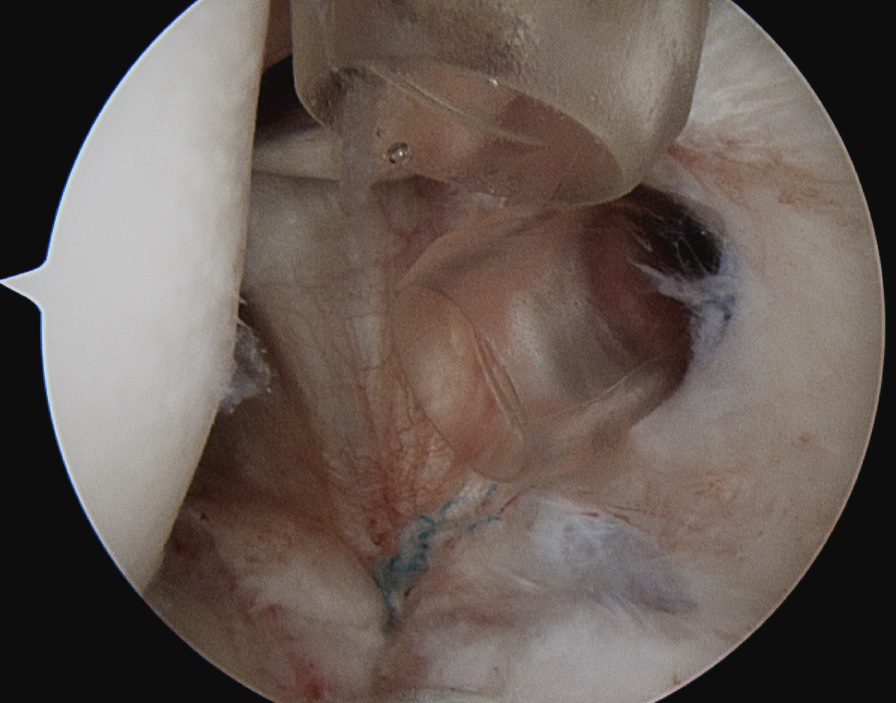
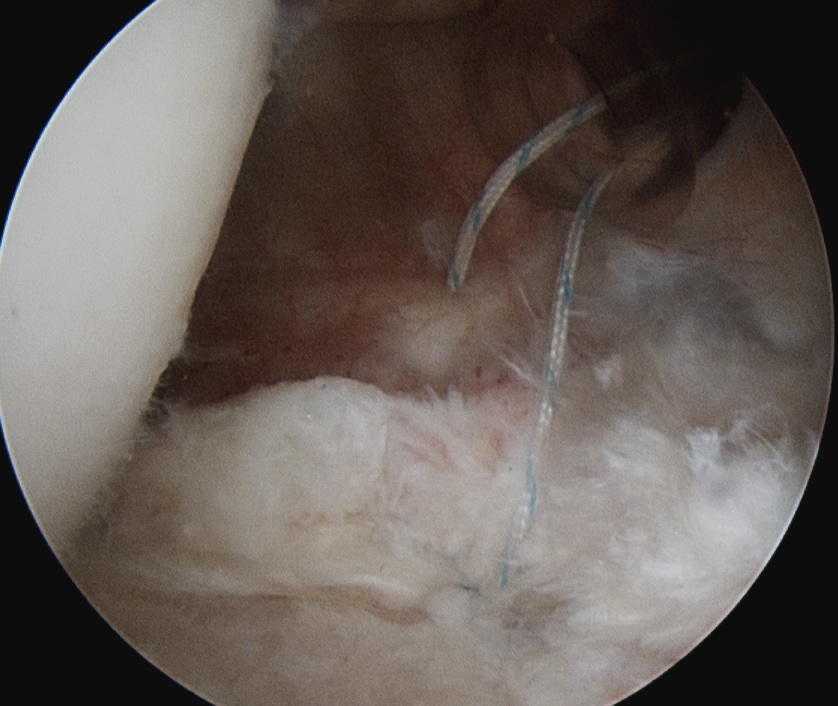
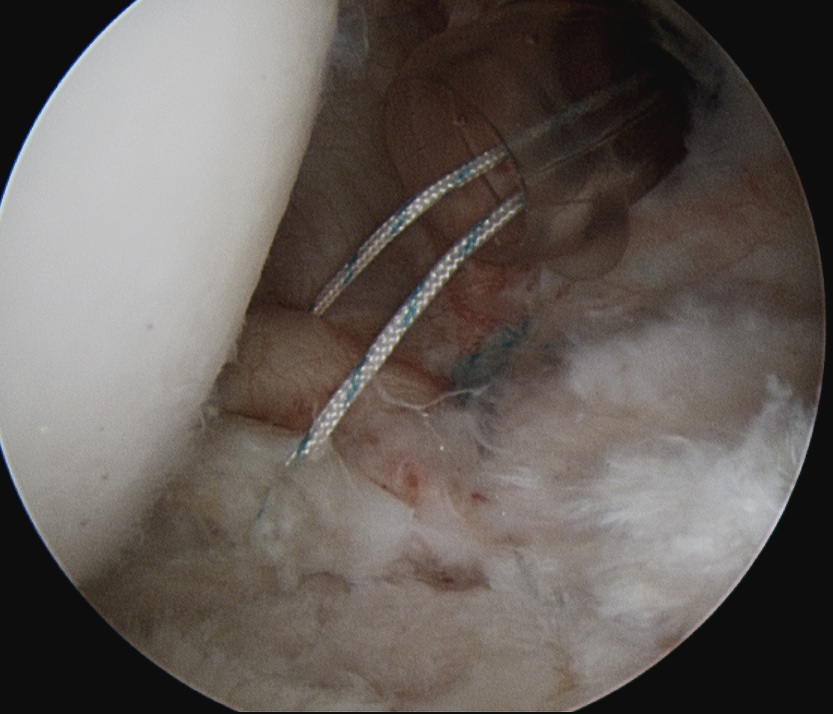
Technique
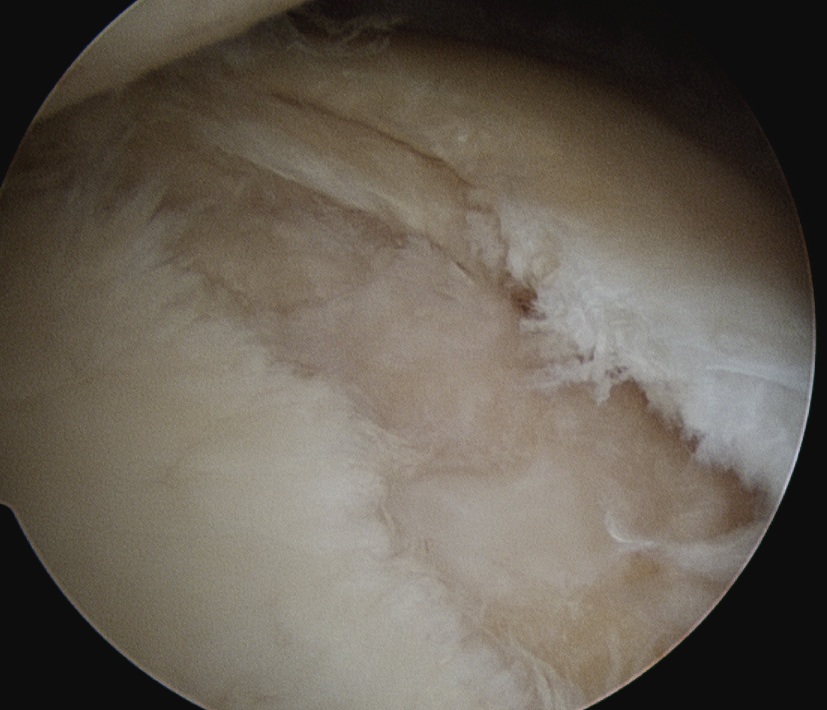
- identify horizontal cleavage tear
- decompress throught tear
- repair labrum
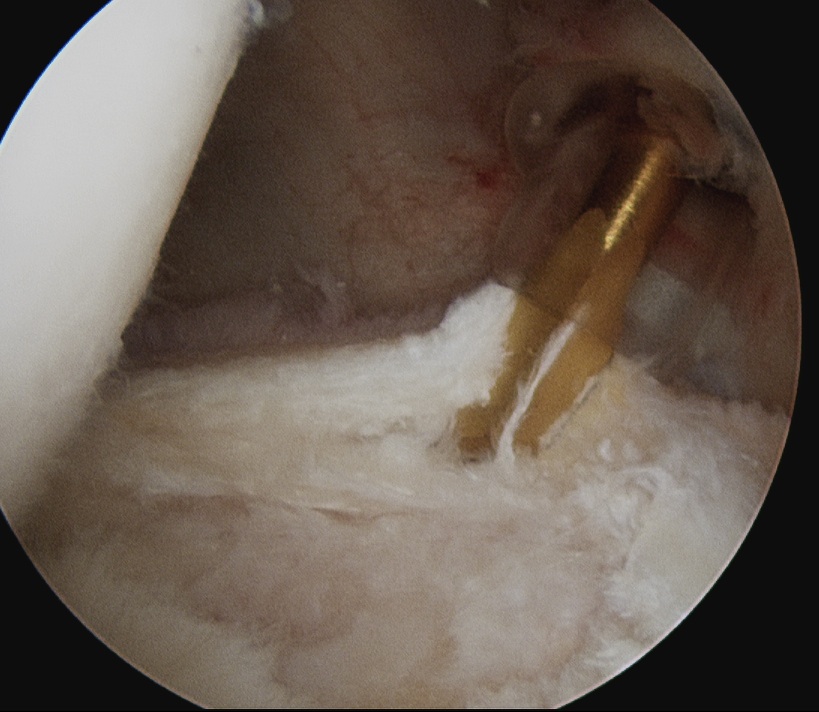
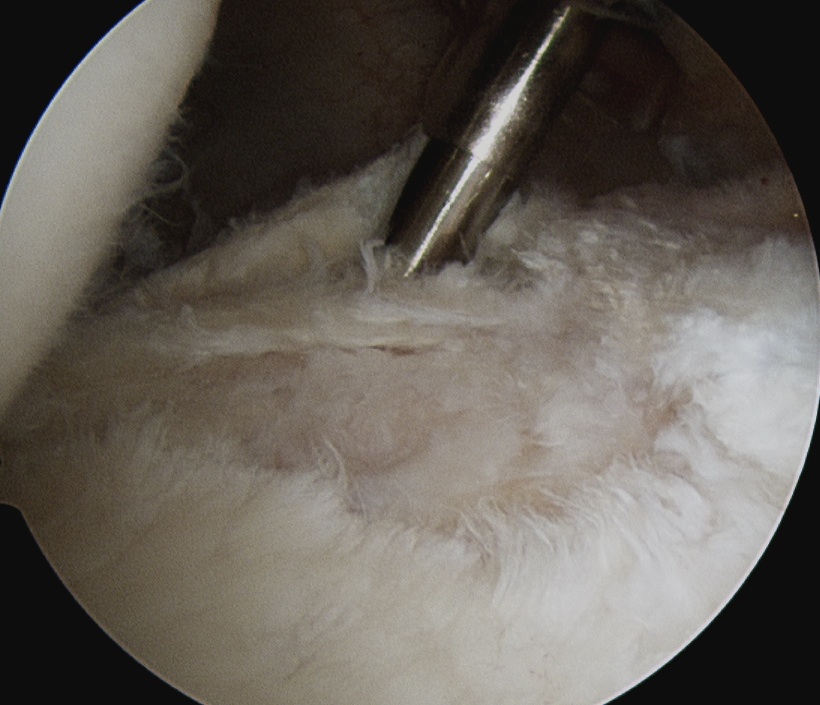
Piatt et al J Should Elbow Surg 2002
- excellent results
Schroder et al JBJS Am 2008
- 42 patients
- posterior labral repair without cyst decompression
- cyst resolved in 88% on MRI and smaller in remainder
- all patients satisfied with outcome
2. Spinoglenoid Cyst without labral tear
Options to decompress cyst
- ultrasound drainage / not always effective but may be worth a try intially
- posterior approach
- arthroscopic glenohumeral approach / posterior capsulotomy
- subacromial approach / between supraspinatous and infraspinatous
Results
Werner et al Arthroscopy 2007
- posterior capsulotomy above IGHL with decompression of cyst with shaver
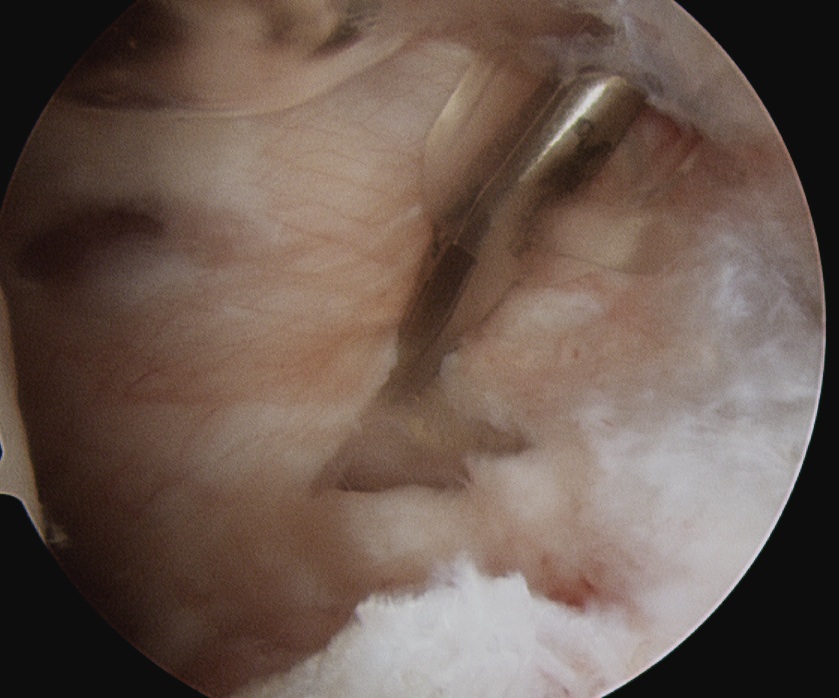
Ghodadra et al Arthroscopy 2009
- subacromial space
- identify spine of scapula
- dissect between infraspinatous and supraspinatous
- accessory posterior portal, retract IS and nerve
- decompress with shaver
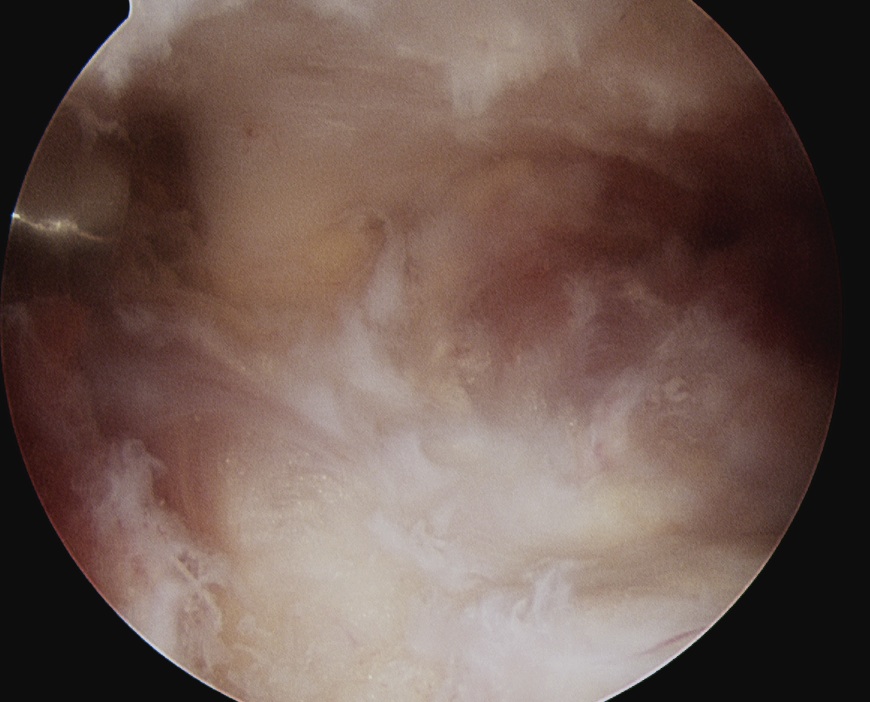
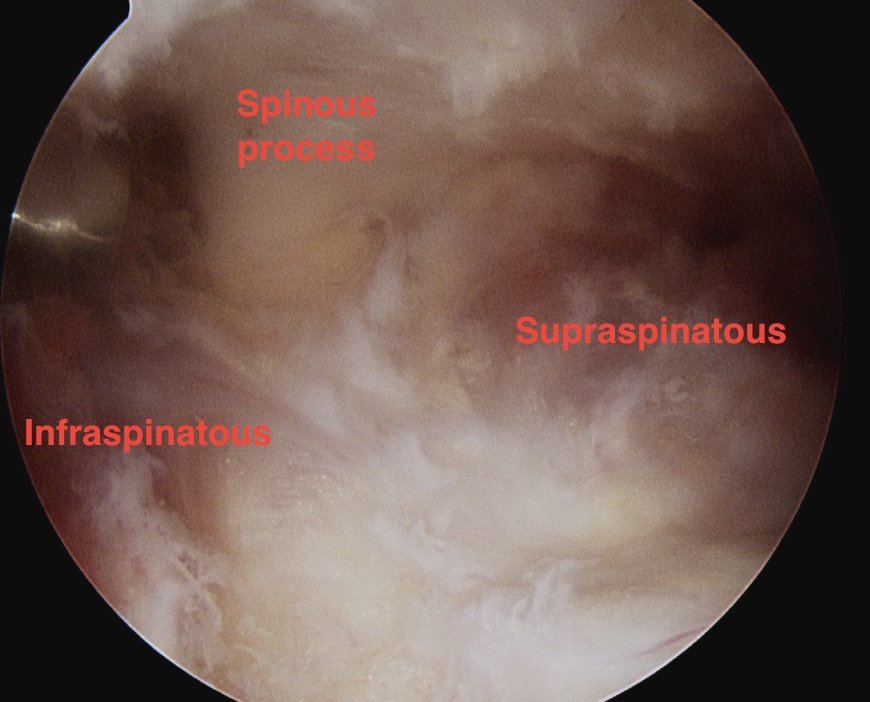
Suprascapular Notch Impingement
Decompression / Division of Suprascapular ligament
Indication
- weakness atrophy of SS and IS without cuff tear
- massive irreparable cuff tear with intractable pain
Options
- open
- arthroscopic
Results
Lafosse et al Arthroscopy 2007
- 10 patients with clinical and EMG evidence of suprascapular nerve compression
- no complications
- good clinical outcome in all patients
Open Technique
- incision along spine of scapular
- sharply elevate trapezius off spine off scapula
- SS reflected inferiorly to expose notch
- preserve superior NV bundle
- suprascapular artery lies above ligament, (branch of Subclavian Artery)
- divide ligament
Arthroscopic Technique
Standard posterior portal
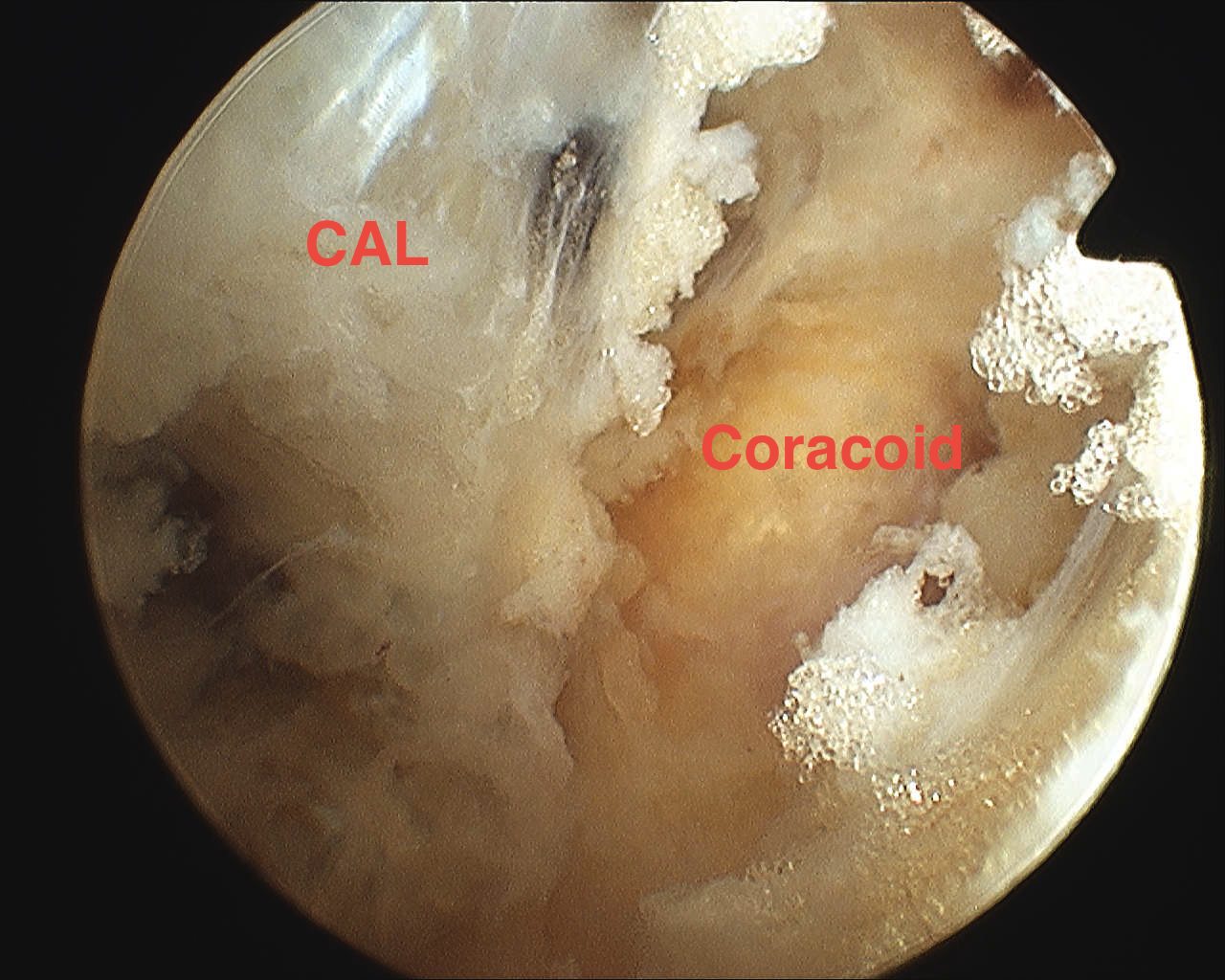
- subacromial portal to debride cuff and identify base of coracoid as landmark
- find coracoid by following CAL to it
- feel hard bony prominence
Anterolateral working portal
- need to be able to work lateral to medial along anterior aspect of humeral head
Dissection
- clear space medial to coracoid along subscapularis
- identify the conoid ligament attaching to the base of the coronoid
- medial to this is fatty area with THL
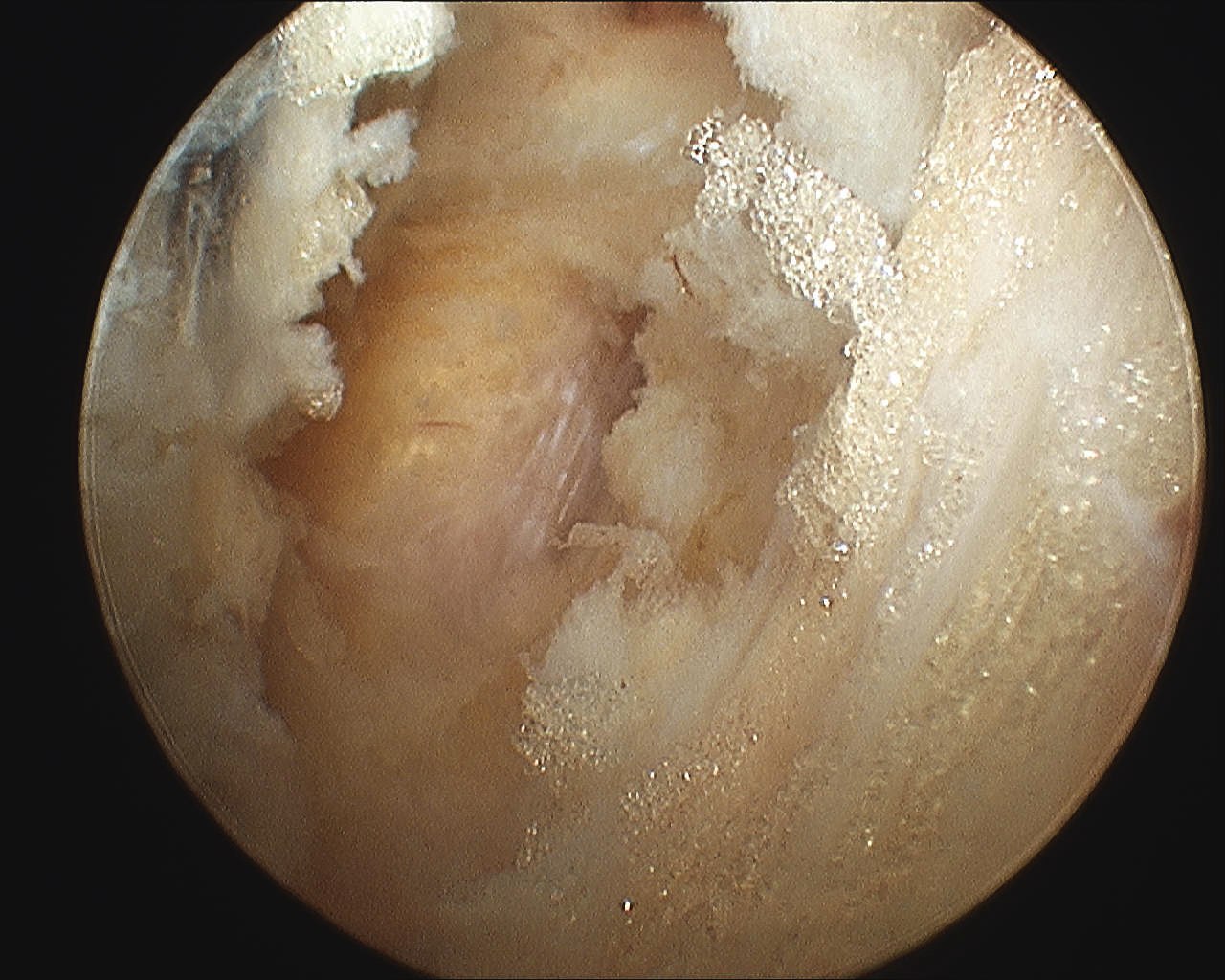
Suprascapular portal / accessory Nevasier
- 7cm from posterior edge of acromion
- insert blunt instruments posteriorly from suprascapular portal
- pass under clavicle
- elevates supraspinous muscle
- use blunt trochar to dissect area
Anatomy
- will usually see the artery passing over the top of the THL
- be careful as this runs from subclavian
- can get torrential bleeding
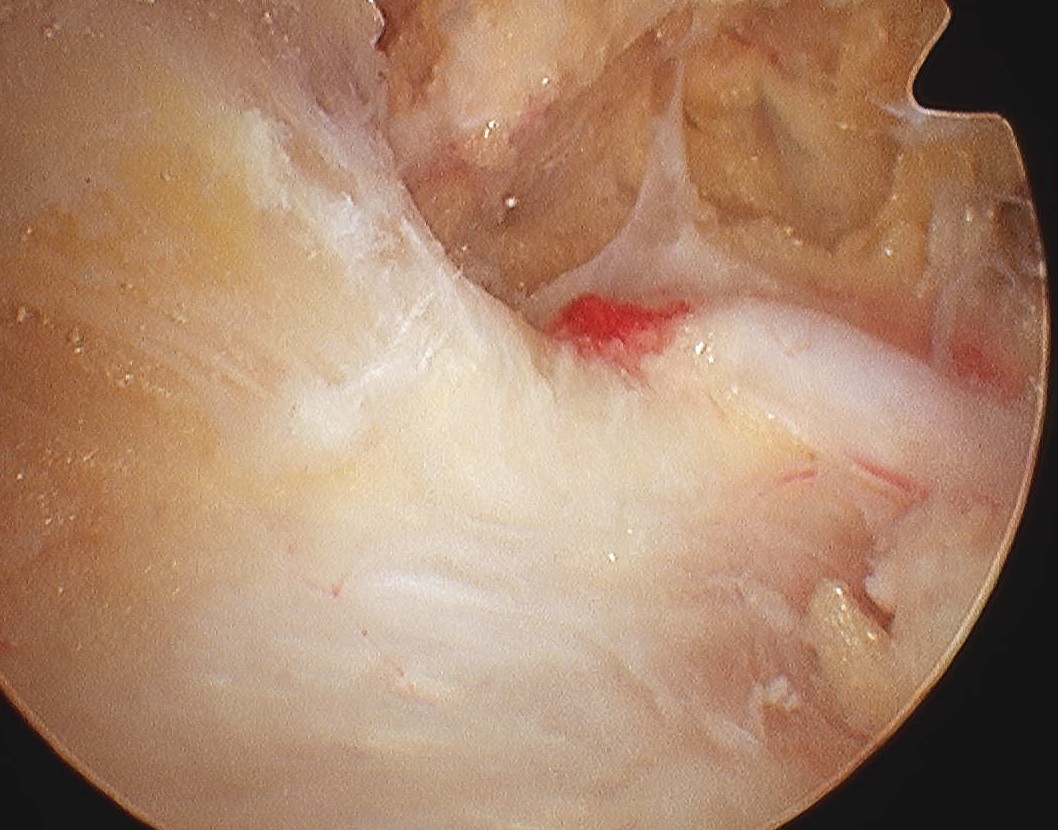
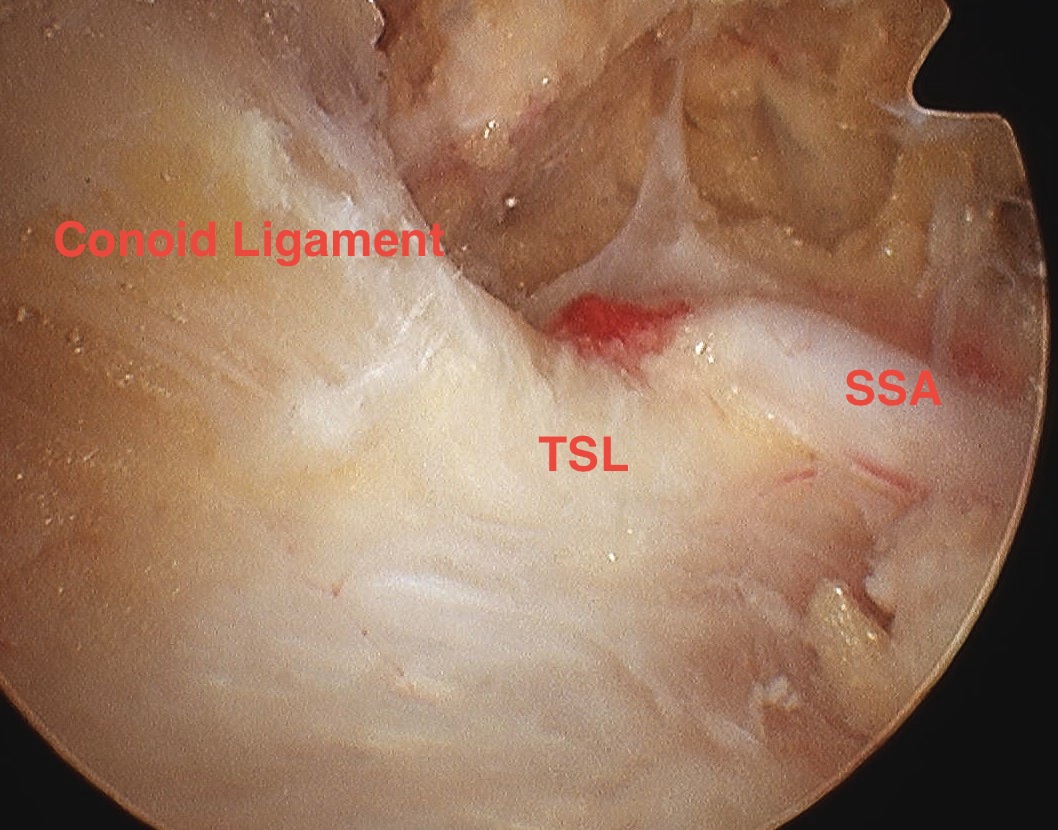
Identify transverse ligament
- identify SSN passing under
- divide TSL with scissors from posterior ACJ portal
- whilst retracting SS artery with probe from SSN portal